
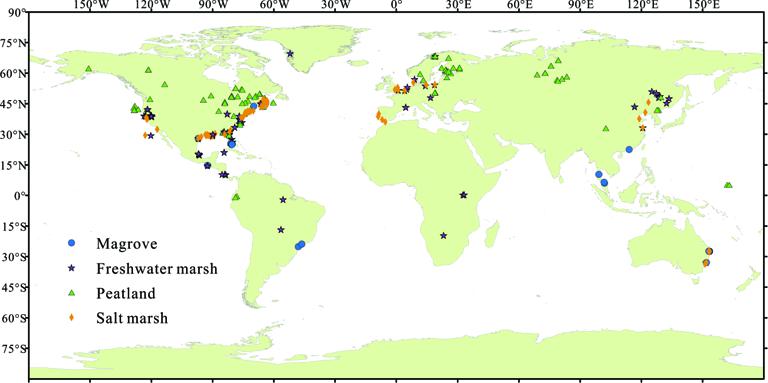
We searched the literatures, up to 31, Dec. 2017, by Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com/) using carbon sequestration or carbon accumulation and wetland (including marsh, fen, tidal marsh, salt marsh, brackish, swamp, bog, fen, mire, peatland, moor) as keywords. Considering soil chronology was generally established by isotopes (137Cs, 210Pb, and 14C), which were suitable for different timescale from decades to millennium years. To make data comparable on the century timescale, only the literatures dated by 137Cs and 210Pb were chosen, and finally, we got 121 valid literatures containing 473 soil/sediment cores from various wetlands. This data contains the following information: Soil sequestration rates g/(m2•yr)), nutrients (N and P)(g/(m2•yr)) accumulation rates and corresponding climate information.
attributes:
Reference as :
CHENG Caifeng, LI Min, XUE Zhenshan, ZHANG Zongsheng, LYU Xianguo, JIANG Ming, ZHANG Hongri, 2020. Impacts of Climate and Nutrients on Carbon Sequestration Rate by Wetlands: A Meta-analysis. Chinese Geographical Science, 30(3): 000–000. doi: 10.1007/s11769-012-0000-0 2019 29(4): 0–0.